- Description
- Additional Information
- Documents
Deaf loop/switch with induction amplifier for hearing aid wearers
If you want to equip a switch with BehiG-Komform, a hearing loop is essential (specifications according to standard SN EN 60118-4: 2015+A1:2018, Standard SIA 500 “Barrier-free buildings”).
Excerpt from the Ordinance of the Federal Department of the Environment, Transport and Communications (DETEC) on the technical requirements for the accessibility of public transport: 151.342, Art. 5, para. 7: In switchboard systems with intercom systems, at least one switch must be equipped with an induction amplifier for the hearing impaired and labelled accordingly.
A hearing loop, also known as a hearing loop, induction loop, induction loop, or T-loop, is an assistive listening device that enables people with a hearing impairment to access facilities. It picks up a sound source and transmits it directly to a hearing aid without background noise. The presence of an induction loop should always be indicated by the symbol on the right.
Hearing loops have become established worldwide as the standard solution for assistive listening in recent years. Due to their advantages and ease of use, those with hearing difficulties are calling for the use of induction loops in public places such as shops, banks, post offices, reception desks, ticket counters, and door intercoms. Proponents are calling for the use of hearing loops in all of the aforementioned locations.
The way an induction loop works is quite simple:
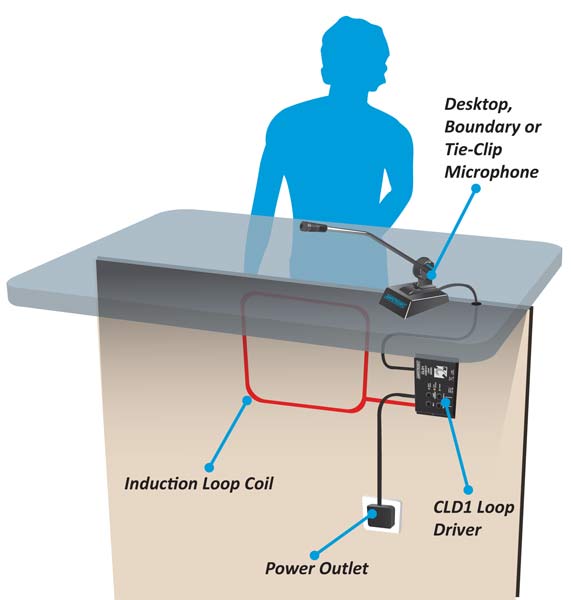
- A sound source, in this case the voice of an employee, is recorded with a directional microphone near his mouth.
- The audio signal is then transmitted to an audio induction loop amplifier, which generates a current to transmit the signal to an induction loop, which usually consists of several turns of copper wire.
- The copper wire induction loop is located (usually) under the switch table on the front panel and generates a magnetic field.
- The magnetic field is picked up by the telephone coil (or T-coil) in the hearing aid of the hearing-impaired listener.
The hearing aid adapts the sound to the specific needs of each individual. Sound is transmitted directly into the ear canal, eliminating background noise and covering the entire frequency spectrum required for intelligibility.
To use the system, a hearing-impaired customer simply needs to set their hearing aid to the "T" position. Expensive receivers are not required, and users don't have to request a headset that identifies them as hearing impaired.
Hearing loops are a simple technology in themselves, but careful design, specification and installation (and expert advice) are required to ensure the system complies with international standards and provides optimal benefit to the end user.
Please contact us, we will be happy to advise you.
Additional information about the product Deaf Loop
distribution: INTECH-ICS AG
Question: Why are hearing loops needed?
Hearing aids are required for any environment where acoustic communication is an integral part of the space, both through legislation for access for people with disabilities, such as z.B. Standard SN EN 60118-4: 2015+A1:2018, as well as through building codes. They help the hearing-impaired, who represent almost one in six people.
Hearing loops are the preferred hearing aid system for the hearing impaired because they are discreet and provide a personalized hearing experience. The user's hearing aid is adjusted to receive the volume and frequency range required.
Question: Isn't that the purpose of hearing aids?
Hearing aids improve sound in close conversation situations or in situations where there is little background noise or the distance to the sound source is close. While modern digital hearing aids can filter out much background noise, they don't solve the problem of the distance between the sound source and the hearing aid, especially in a busy store. A hearing loop magnetically and seamlessly transmits sound from a microphone, television, or audio signal directly to hearing aids and cochlear implants.
Question: How much does an induction loop cost?
The cost of an induction loop system depends on the complexity of the required installation and the quality of the components. Please request a quote here.
Question: How are they installed?
Induction loop systems consist of three main components required for installation: the microphone, the amplifier, and the loop. The microphone's selection and positioning are critical to obtaining a clean signal without background noise. The microphone is typically mounted on the countertop. The amplifier and loop are typically mounted under the counter at the front (facing the customer) and may require additional cabling to access a power source.
Question: Can I install it myself?
You can purchase a counter loop and install it yourself; however, it's always worth consulting us first. The selection and positioning of the microphone and loop are crucial for a successful installation and depend on the dimensions and construction of the counter (especially with metal counters). The system must meet international performance standards; if it doesn't, it cannot be considered functional and does not comply with the Equality Act.
Question: Does interference from electrical devices prevent the magnetic field from functioning?
In some cases, the environment may contain a large amount of cable or high-voltage current, making an induction loop either uneconomical or unsuitable. However, with the use of modern equipment and proper design, these cases are very limited.
Question: Can multiple hearing loops be in the same room?
The magnetic field generated by a deaf loop can spill over into adjacent areas and cause interference with other, very nearby induction loops. It is possible to install induction loops directly next to each other. This depends on the dimensions of the switch and the extent of the field spillover.
Question: What is meant by "magnetic field"?
A hearing loop works by creating a magnetic field that "spreads" toward the user. The loop must be placed in a specific location, and the current adjusted to create a field strength that corresponds to the position where the user's hearing aid will be located.
Question: Do all hearing aids have a telecoil?
The increasing popularity of induction loops has led to more and more hearing aids being equipped with telephone coils.Currently, almost 70% of hearing aid models on the market are equipped with them. In countries where hearing loops are already established, this figure rises to 95%, and all new cochlear implant models now feature telecoils.
Question: Don't wireless technologies like Bluetooth offer a simpler and less expensive solution?
Wireless technologies in their current form are not suitable for hearing aids because they cause significant battery drain and have a limited range. In the case of Bluetooth, for example, the range is between 5 and 100 square meters (depending on the type), the technology can only support up to seven users simultaneously, and also requires pairing devices to connect.


 Brochure Deaf Loop/Switch with Induction Amplifier for Hearing Aid Wearers - German
Brochure Deaf Loop/Switch with Induction Amplifier for Hearing Aid Wearers - German 
